Lambda: Language Models Bridging Data Workshop
Join Us on September 27 and 28 (Wed and Thu)
@ LT15,
School of Computing,
National University of Singapore
Free Registration
About
The importance of developing effective and efficient ways of understanding and utilizing data cannot be overstated. Despite the significant amount of parametric knowledge that can be accessed through large language models (LLMs), there is an even larger reservoir of external or private data waiting to be queried. The Lambda workshop explores the frontier of research in natural language processing and data management where language models serve as the nexus between diverse data types.
This workshop seeks to engage researchers, practitioners, and enthusiasts alike, diving into how language models can be leveraged to bridge and enhance the access of structured and unstructured data at scale. A primary question we seek to discuss and understand in this workshop is "How can LLMs enhance data management systems and vice versa?" Other topics of interest include:
- How do we query structured and unstructured data with LLMs or with SQL? What are the use cases?
- Where do we find or how do we properly create benchmark data for querying LLMs with external data (e.g., personal timeline data)?
- How can LLMs advance the state-of-the-art in database research problems such as data integration?
This will be the first workshop on this topic in Singapore and also the first workshop to bring all local DB and NLP researchers together to discuss this topic. The workshop will feature invited talks and lightning talks from researchers in this area and we hope to foster plenty of opportunities for discussions. The detailed two-day program, which will feature four invited speakers, will be announced soon.
Program Schedule
| Day 1 (27 Sep) | Program | Speaker |
|---|---|---|
| 8:00am | Registration | |
| 8:45am to 9:00am | Welcome | Kian Lee Tan |
| 9:00am to 10:00am Keynote 1 |
Structured Knowledge and Data Management for Effective AI Systems | Ihab Ilyas |
| 10:00am to 10:30am | Break | |
| 10:30 to 12:30pm Session 1 |
Representing ASEAN - Building a Regionally-Oriented Small LLM | Leslie Teo and William Tjhi |
| Navigating Challenges in LLMs: Problems and Directions | Lu Wei | |
| 12:30pm to 2:30pm | Lunch | |
| 2:30pm to 3:30pm Tutorial |
A Primer on Retrieval-augmented Modelling Techniques | Patrick Lewis |
| 3:30pm to 4:00pm | Break | |
| 4:00pm to 5:00pm Keynote 2 |
Building Modern Retrieval-Augmented LLM APIs | Patrick Lewis |
| Day 2 (28 Sep) | Program | Speaker |
| 9:00am to 10:00am Keynote 3 |
The Role of Large Language Models in Building the Well-Being Operating System | Alon Halevy |
| 10:00am to 10:30am | Break | |
| 10:30am to 12:00pm Session 2 |
Inferring Cancer Disease Response from Radiology Reports Using Large Language Models | Ng Hwee Tou |
| A short history of LLMs and Instruction Tuning | Jason Phang | |
| 12:00pm to 2:30pm | Lunch | |
| 2:30pm to 3:30pm Keynote 4 |
Evaluation and Application of Pre-trained Large Vision-Language Models | Jing Jiang |
| 3:30pm to 4:00pm | Break | |
| 4:00pm to 4:30pm | Lightning Session/Open Discussion |
Organized By
Keynote 1
Structured Knowledge and Data Management for Effective AI Systems
Can structured data management play an important role in accelerating AI? In this talk I focus on two main aspects of structured data management and argue that they are key in powering and accelerating AI application development: 1) Automating data quality and cleaning using generative models; and 2) constructing and serving structured knowledge graphs and their role in semantic annotation and grounding unstructured data. In the first thrust, I will summarize our findings building the HoloClean project. HoloClean builds generative probabilistic models describing how data was intended to look like, and use them for predicting errors and repairs. On the structured knowledge front, I will describe our work building Saga, an end-to-end platform for incremental and continuous construction of large scale knowledge graphs. Saga demonstrates the complexity of building such platform in industrial settings with strong consistency, latency, and coverage requirements. I will discuss challenges around building entity linking and fusion pipelines for constructing coherent knowledge graphs; updating the knowledge graphs with real-time streams; and finally, exposing the constructed knowledge via ML-based entity disambiguation and semantic annotation. I will also show how to query such knowledge via vector representation capable of handling hybrid similarity/filtering workloads.
Ihab Ilyas
Apple
University of Waterloo
Ihab Ilyas is a professor in the Cheriton School of Computer Science and the NSERC-Thomson Reuters Research Chair on data quality at the University of Waterloo. He is currently on leave as a Distinguished Engineer at Apple, where he lead the Knowledge Graph Platform team. His main research focuses on data science and and data management, with special interest in data cleaning and integration, knowledge construction, and machine learning for structured data management. Ihab is a co-founder of Tamr, a startup focusing on large-scale data integration, and he is also the co-founder of inductiv (acquired by Apple), a Waterloo-based startup on using AI for structured data cleaning. He is a recipient of the Ontario Early Researcher Award, a Cheriton Faculty Fellowship, an NSERC Discovery Accelerator Award, and a Google Faculty Award, and he is an ACM Fellow and an IEEE Fellow.
Session 1
Representing ASEAN - Building a Regionally-Oriented Small LLM
We detail the development of a set of LLMs tailored to ASEAN, in particular, a 3 billion and 13 billion parameter model which is currently being trained. Our model was trained on a dataset of over 1.3 trillion tokens compiled from MC4 and regional sources including local news, government documents, social media, and books/articles related to our geography and culture. In addition to the model, we also introduced a new benchmark, and trained a tokenizer. We employed MPT, using MosaicComposer, on 256 GPUs. The model is targeted to be released in mid November this year. But we can share some of the initial lessons learned by the team.
Leslie Teo
AI Singapore
Leslie coaches the AI SG Products team, having pivoted from a career in economics, finance, and investing in 2019. That year, he joined Grab as Head of Data Science, Policy, and Data Initiatives and Advisor to the CEO. In that role, he sought to answer critical business and social questions using data and build products that provided relevant insights, such as congestion patterns and creating safer bike paths. He helped lay the foundation for the data science and analytics role at Grab and Singtel’s digital bank (GxS). After Grab, Leslie was Managing Director at Great Eastern Life Insurance for Data and Strategic Transformation. Leslie was the Director of the Economics and Investment Strategy Department and Chief Economist at GIC Private Limited. He and his team were responsible for formulating and implementing GIC’s new investment model, the first revision in over two decades. He remains an advisor to the government on reserve management issues. Leslie was also at the MAS and IMF. Leslie has a Liberal Arts and Sciences degree from the University of Chicago and a Ph.D. in Economics and Finance from the University of Rochester. He has a Master's in Information and Data Science from the University of California at Berkeley.
William Tjhi
AI Singapore
William Tjhi has been practicing machine learning to solve industry problems for 15 years. He received his PhD from NTU in 2008, with a thesis on unsupervised learning for text data. He spent a few years with A*STAR IHPC where he learned how to scale up ML with distributed systems. When in GovTech, he was a part of the unit that prototyped the analytics component of the municipal service system and was instrumental in the setting up of the data science team in SPRING (now EnterpriseSG). For a while, William was also the lead NLP at the Indonesian unicorn startup Traveloka. There, he appreciated the challenges of doing NLP in the then low- resource Bahasa Indonesia. This became an inspiration for him when he later initiated Project Southeast Asia CoreNLP (SEA CoreNLP) in AI Singapore. In the early days of AI Singapore, he was one of the first engineers that set the foundation for the execution of the 100 Experiments and AI Apprenticeship Programme. Today, William leads the research work on LLMs in the AI Products division of AI Singapore. He also holds a technical advisor position with ASEAN Applied Research Centre, and a part-time ML consultant to a stealth tech startup built by the co- co-founder of Traveloka. In his spare time, William contributes regularly to tech communities like the AI Professional Association in Singapore, Project Bahasa Indonesia NLP Alliance (ProjectBINA) and Data Science Indonesia (DSI) in Jakarta.
Session 1
Navigating Challenges in LLMs: Problems and Directions
I will discuss some challenges associated with the current state of LLMs and offer our perspectives on them. Specifically, I will share some of our recent endeavors that center around the following research themes:
- Structures: Modern chat models are great at many things but are recognized that they may encounter challenges in tasks such as structured prediction. I’ll discuss some theoretical limitations with such models while offering some observations on the strong potential of alternative models such as masked language models for such tasks. Based on that, I’ll share some perspectives on how to improve chat models’ capabilities on such tasks.
- Reasoning: The chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting method demonstrates LLMs’ capabilities to carry out step-by-step reasoning. We argue that LLMs may be able to perform structured multi-dimensional reasoning, which is demonstrated by our Tab-CoT prompting mechanism. We discuss how this may serve as a step towards better understanding the emergent behaviours of LLMs, one of the most fundamental research problems in LLMs.
- Fine-tuning: While various parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods are successfully proposed, the feasibility of achieving further storage reduction remains a research question. We have identified an approach that can be applied to all existing PEFT techniques, demonstrating its effectiveness in significantly reducing the storage requirements for additional parameters.
- Pre-training: I'll discuss some of our ongoing efforts to investigate better ways to effectively pre-train LLMs. One of our current focuses is to build effective yet relatively small LLMs. I will elaborate on the significance of such a direction, how such models may benefit the community, and what their practical implications could be.
Lu Wei
Singapore University of Technology and Design
Wei Lu is currently an Associate Professor and Associate Head (Research) of the Information Systems Technology and Design Pillar of Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD). He is also the Director of the StatNLP Research Group, which focuses on fundamental research on Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Large Language Models (LLMs). He is currently serving as an Action Editor for Computational Linguistics (CL) and Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics (TACL). He served as a Senior Area Chair for ACL, EMNLP, and NAACL. He also served as a PC Chair for NLPCC and IJCNLP/AACL. He received the Best Paper Award at EMNLP 2011 (top 0.16%), Best System Paper Award at SemEval 2022 (top 0.45%), and Area Chair Award (‘Resources and Evaluation’ Area) at ACL 2023 (top 0.42% within the area).
Tutorial
A Primer on Retrieval-augmented Modelling Techniques
In this session, we’ll cover a number of techniques from the (relatively-recent) literature for building retrieval augmented models, as well as some historical perspective. We will highlight motivations, key concepts and design challenges underpinning this area, and use a few case study models and papers to illustrate and explore how to tackle them. This session is designed to provide context and grounding for those interested in working in this area, and act as an optional primer for the keynote talk.
Keynote 2
Building Modern Retrieval-Augmented LLM APIs
In this talk, I will describe how to build effective and powerful retrieval-augmented systems leveraging modern state-of-the art large language models. This talk will draw on recent experiences from building Cohere’s Retrieval-augmented LLM API, and discuss my takes on the strengths, limitations and best practices when leveraging retrieval augmentation for real-world applications.
Patrick Lewis
Cohere
University College London
Patrick Lewis is an NLP and AI Research Scientist based in London, and leads the Retrieval-Augmented Modelling team at Cohere. Previously, He was a Research Scientist at the Fundamental AI Research Lab (FAIR) in Meta for 4 years, and received his PhD at UCL and FAIR, under the supervision of Sebastian Riedel and Pontus Stenetorp. Patrick works at the intersection of information retrieval techniques (IR) and large language models (LLMs), and has worked extensively on Retrieval-Augmented Language Models. He is interested in how to represent, store and retrieve, knowledge for use with large language models. His work focuses on building more powerful, efficient, robust, private and updatable models that can not only perform well on a wide range of tasks, but provide providence and cite their sources. Such models should excel on knowledge-intensive NLP tasks – NLP tasks that require a substantial amount of world knowledge to do well on, and which an average human would require access to a search engine, library or external knowledge source to do well.
Keynote 3
The Role of Large Language Models in Building the Well-Being Operating System
Many applications claim to enhance our well-being, whether directly, like aiding meditation and exercise, or indirectly, such as guiding us to our destinations or managing daily tasks. However, the truth is that the potential of technology to improve our well-being often eludes us. We find ourselves more distracted than ever, spending excessive time ruminating on minutiae in our lives, and struggling to be fully present and relish the moment. Part of this issue arises from the fact that each of these apps focuses on a specific aspect of well-being without any coordination among them. This situation parallels the early days of computer programming when each program interacted directly with the computer's hardware. Drawing from this analogy, I will start this talk by outlining a set of mechanisms that can facilitate better collaboration among these applications, essentially proposing an operating system for well-being. This operating system comprises a data repository (called, a personal timeline) for your past experiences and future aspirations, mechanisms for utilizing your personal data to provide improved recommendations and life plans, and, lastly, a module to assist you in navigating and nurturing essential relationships in your life. The talk will then focus on the first component of the operating system, namely the timeline of your life experiences. We will cover our open-source TimelineBuilder, a system that lets you import a lot of your personal digital data, visualize it and ask questions about your past. In doing so, we will identify opportunities for language models to be a core component on which we build systems for querying personal timelines and for supporting other components of the operating system.
Alon Halevy
Meta Reality Labs Research
Alon Halevy is a director at Meta’s Reality Labs Research, where he works on Personal Digital Data, the combination of neural and symbolic techniques for data management and on Human Value Alignment. Prior to Meta, Alon was the CEO of Megagon Labs (2015-2018) and led the Structured Data Group at Google Research (2005-2015), where the team developed WebTables and Google Fusion Tables. From 1998 to 2005 he was a professor at the University of Washington, where he founded the database group. Alon is a founder of two startups, Nimble Technology and Transformic (acquired by Google in 2005). Alon co-authored two books: The Infinite Emotions of Coffee and Principles of Data Integration. In 2021 he received the Edgar F. Codd SIGMOD Innovations Award. Alon is a Fellow of the ACM and a recipient of the PECASE award and Sloan Fellowship. Together with his co-authors, he received VLDB 10-year best paper awards for the 2008 paper on WebTables and for the 1996 paper on the Information Manifold data integration system.
Session 2
Inferring Cancer Disease Response from Radiology Reports Using Large Language Models
In this talk, I will present our work on inferring cancer disease response (one of no evidence of disease, partial response, stable disease, or progressive disease), given a radiology report written in English. Our novel approach uses a large language model, GatorTron transformer, pre-trained on clinical texts. We also employed data augmentation using sentence permutation with consistency loss as well as prompt-based fine-tuning. We assembled 10,602 computed tomography reports from cancer patients in our study. Empirical evaluation shows that our approach achieves classification accuracy close to 90%. This work was done in collaboration with cancer specialist doctors at the National Cancer Centre Singapore and Duke-NUS Medical School.
Ng Hwee Tou
National University of Singapore
Professor Ng Hwee Tou is Provost's Chair Professor of Computer Science at the National University of Singapore (NUS). He received a PhD in Computer Science from the University of Texas at Austin, USA. His research focuses on natural language processing. He is a Fellow of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), and the editor-in-chief of Computational Linguistics journal.
Session 2
A short history of LLMs and Instruction Tuning
This talk will provide a short (and opinionated!) history of the research developments before and around instruction tuning, and how we got to the point of building general-purpose chat-assistant LLMs. This talk will contextualize the developments from the early pretrain-and-finetune paradigms of GPT-1 and BERT, all the way to modern models such as ChatGPT/GPT-4 and LLAMA/2 variants such as Vicuna and Platypus.
Jason Phang
NYU Center for Data Science
Jason Phang is a fifth-year PhD Student at the NYU Center for Data Science advised by Sam Bowman. He is a member of the NYU Alignment Research Group, and a Research Scientist at EleutherAI. He actively works on researching transfer-learning with LLMs and open-source LLM development.
Keynote 4
Evaluation and Application of Pre-trained Large Vision-Language Models
Recent years have witnessed remarkable progress in natural language processing and computer vision, powered by pre-trained foundation models that have demonstrated strong generalization capabilities for downstream tasks. In addition to Large Language Models (LLMs), such as ChatGPT, that are now widely adopted by the public, there are also Large Vision-Language Models, such as CLIP, that have strong capabilities to process and comprehend images and text simultaneously. In this talk, I will first briefly introduce these Large Vision-Language Models. I will then present our recent work that aims to measure the degree of stereotypical biases in these Large Vision-Language Models. Next, I will present another piece of work that applies pre-trained vision-language models under zero-shot settings to visual question answering. I will conclude the talk by pointing out some future directions in evaluating and applying pre-trained Large Vision-Language Models.
Jing Jiang
Singapore Management University
Jing Jiang is a Professor of Computer Science and the Director of the AI and Data Science Cluster in the School of Computing and Information Systems at the Singapore Management University (SMU). She was in the list of Singapore’s 100 Women in Tech in 2021. Her research interests include natural language processing, text mining, and machine learning. She has received two Test of Time paper awards for her work on social media analysis. She currently serves as an Action Editor of the Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics (TACL). She previously served as a Program Chair of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) in 2019 and was a member of the editorial board of Computational Linguistics.
Location
LT 15, 11 Computing Drive (Block AS6), Singapore 117416
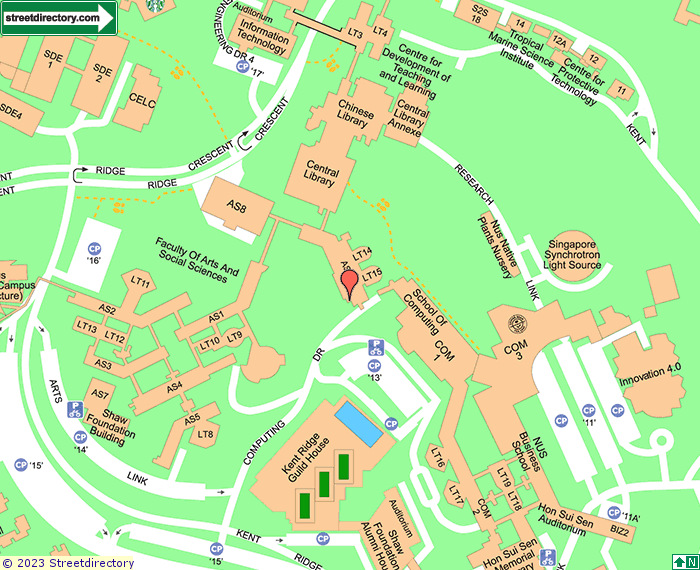

Please click 'Getting Here' for detailed instructions on how to reach LT15.
View on Map Getting Here